Achieving black box vertical federated learning
Wednesday, March 02, 2022

When you hear the term “black box,” most people think about the flight data recorder of an airplane. Mohamed bin Zayed University of Artificial Intelligence (MBZUAI) Assistant Professor of Machine Learning, Dr. Bin Gu, thinks about algorithms and optimization. In computer science, black-box optimization (BBO) considers the design and analysis of algorithms for problems where the structure of the objective function and/or the constraints defining the set is unknown, un-exploitable, or non-existent (Science Direct).
Large-scale optimization
Gu has a special interest in exploring large-scale optimization techniques on bi-level optimization and black-box optimization problems to solve some of the most important machine learning tasks—automated machine learning, reinforcement learning and spiking neural networks.
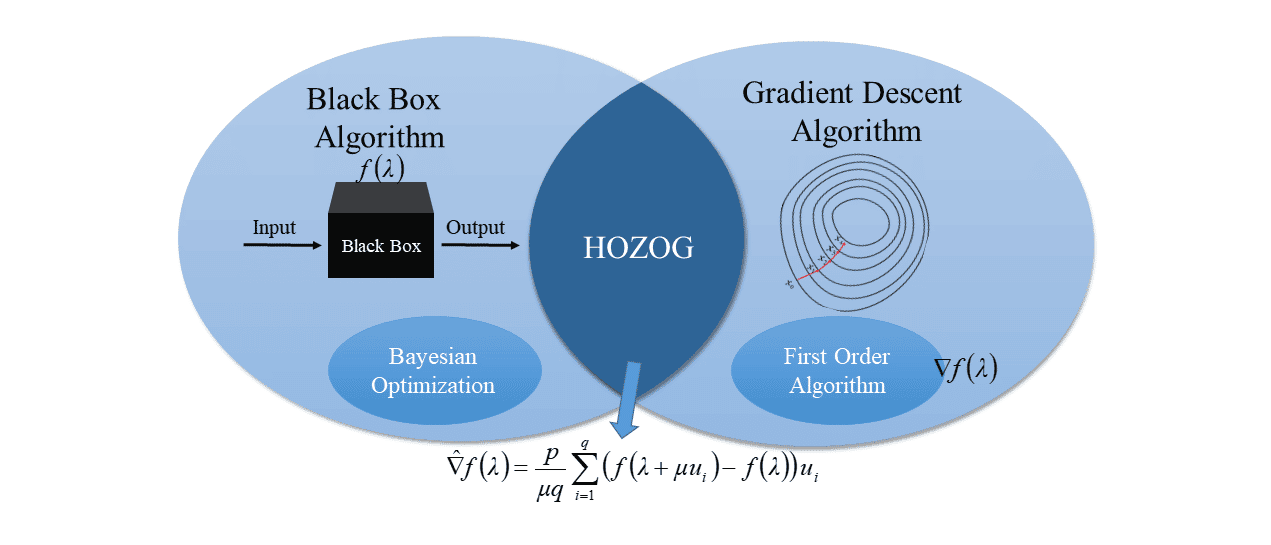
“Where bilevel optimization is the fundamental mathematical problem to achieve automatic machine learning, black box optimization is especially important to machine learning due to the privacy of learning models,” Gu said.
[wps_pull-out-quotes-left content=”Alongside my students, we hope to bring machine automation closer to the way the human brain operates.” surname=”Dr. Bin Gu” source=”MBZUAI Assistant Professor of Machine Learning”][/wps_pull-out-quotes-left]Black-box optimization is a rapidly growing field of optimization and critical in many sectors such as energy, the environment, systems engineering, computational biology, drug discovery, and chemical synthesis. And Gu’s work has had some success. “We have already connected black box optimization and vertical federated learning, and achieved black box vertical federated learning which can keep data and model privacy as much as possible,” Gu continued. “This work was collaborated with JD.com – the second largest e-commerce company in China.”
Large-scale machine learning
Gu received his B.S. and Ph.D. degrees in computer science from the Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, in 2005 and 2011, respectively. He worked as a postdoctoral fellow at the University of Western Ontario; at the University of Texas at Arlington; and at the University of Pittsburgh.
“Alongside my students, we hope to bring machine automation closer to the way the human brain operates. We have two current projects. One is large scale optimization in machine learning, and the other one is spiking neural networks.”
Gu joined MBZUAI in 2020, having previously worked as a full professor at Nanjing University of Information Science and Technology in China. Gu has published more than 70 papers, with 3000-plus citations. He served as a program committee member or reviewer for several leading machine learning and data mining conferences and journals such as NIPS, ICML, KDD, AAAI, TPAMI, JMLR, and a senior program committee member of IJCAI 2019-2021.
“In machine learning, the next step in my mind is understanding neural networks, designing human-like brain neural networks, and achieving automatic large scale machine learning,” Gu said.
- machine learning ,
- black box ,
- gu ,
Related
The search for an antidote to Byzantine attacks
A new study from MBZUAI and other institutions tackles malicious and faulty updates in privacy-preserving machine learning.....
Read MoreAI and the silver screen: how cinema has imagined intelligent machines
Movies have given audiences countless visions of how artificial intelligence might affect our lives. Here are some.....
- cinema ,
- art ,
- fiction ,
- science fiction ,
- AI ,
- artificial intelligence ,
Mind meld: agentic communication through thoughts instead of words
A NeurIPS 2025 study by MBZUAI shows that tapping into agents’ internal structures dramatically improves multi-agent decision-making.
- machine learning ,
- neurips ,
- agents ,


