AI foundation model GluFormer outperforms clinical standards in forecasting diabetes and cardiovascular risk
Thursday, January 15, 2026
A study published in Nature and co-led by researchers at MBZUAI demonstrates that an AI foundation model trained on continuous glucose monitoring (CGM) data can predict long-term diabetes and cardiovascular risk more accurately than current clinical standards.
Built using extensive datasets from the Human Phenotype Project (HPP), the model, GluFormer, uses short-term glucose dynamics to forecast individual health risks, including the likelihood of developing diabetes or facing an increased risk of cardiovascular-related death up to 12 years later.
Eran Segal, Hagai Rossman and Eric Xing, co-authors of the paper, highlight how continuous physiological data can reveal early disease risk and support personalized prevention and care for metabolic conditions.
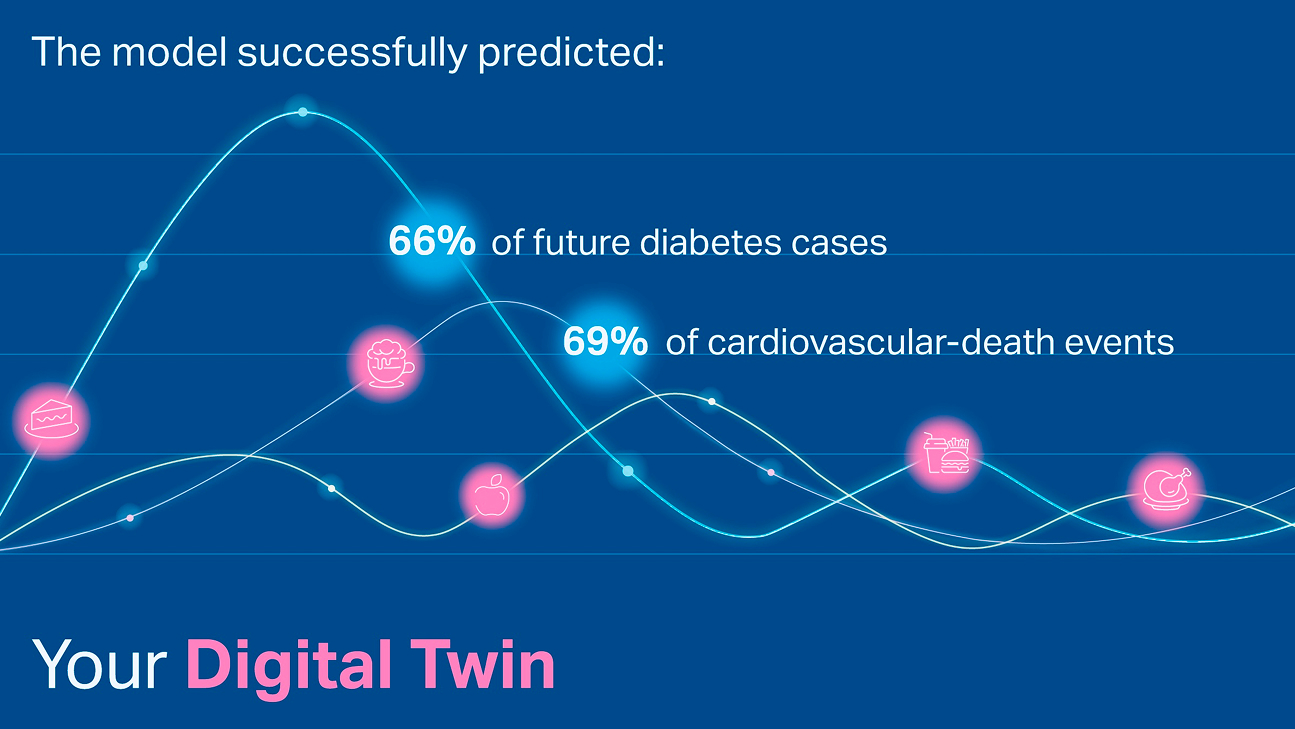
GluFormer, built on a transformer architecture, was trained using NVIDIA AI infrastructure on over 10 million CGM measurements from 10,812 participants, primarily without diabetes, within the HPP cohort. In a 12-year follow-up of 580 adults, the model’s predictions captured 66 per cent of new-onset diabetes cases and 69 per cent of cardiovascular-death events in its highest-risk group, while no cardiovascular-deaths occurred in the lowest-risk group.
The model was further evaluated across 19 external cohorts representing diverse populations, devices, and metabolic states. Across these settings, GluFormer consistently outperformed established CGM-derived metrics in predicting clinical outcomes such as fasting glucose, visceral fat, liver attenuation, kidney markers, and lipid levels.
Eran Segal, Professor of Computational Biology at MBZUAI, said: “The development of GluFormer is a major step forward, leveraging the deep and dynamic data collected by the Human Phenotype Project to move beyond simple point-in-time measurements. This work shows how, by analyzing glucose dynamics directly rather than relying on summary metrics, we gain a clearer view of each individual’s underlying risk trajectory.
“GluFormer’s ability to predict clinical outcomes up to four years in advance, outperforming established clinical standards like GMI, provides unparalleled insight into individual metabolic trajectories, paving the way for truly proactive and personalized health strategies and intervention.”
Key highlights of GluFormer to capture subtle metabolic signals that offer powerful predictive insights include:
- Predicting future diabetes: In a 12-year longitudinal study (the AEGIS cohort), GluFormer’s risk stratification proved significantly more effective than standard blood HbA1C% measurements. The model successfully captured 66% of all new-onset diabetes diagnoses that occurred over the 12 years among the top risk quartile identified.
- Forecasting cardiovascular death: The model similarly stratified risk for severe cardiometabolic outcomes, with 69% of cardiovascular-death events occurring in the top quarter identified by GluFormer, and zero events detected in the bottom quartile.
- Long-term prognosis: GluFormer consistently outperforms the current clinical standard for CGM analysis, the Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), in forecasting a wide array of clinical measures, including visceral adipose tissue (VAT) and fasting glucose levels, up to four years in the future.
- Advances personalized diet planning: By developing a multimodal version that integrates comprehensive dietary data with glucose readings, the model can generate simulated CGM responses to specific foods, enhancing prediction accuracy significantly, particularly around meal times.
This project was a collaboration between researchers from MBZUAI, Weizmann Institute of Science and NVIDIA.
- health ,
- foundation models ,
- nature ,
- HPP ,
- diabetes ,
- cardiovascular ,
- digital public health ,
Related
MBZUAI launches K2 Think V2: UAE’s fully sovereign, next-generation reasoning system
The 70-billion parameter advanced reasoning system is now built on the K2-V2 base model – the Institute of.....
Read MoreK2 Think V2: a fully sovereign reasoning model
MBZUAI's Institute of Foundation Models has released its first fully sovereign reasoning model with a new version of K2 Think.
- K2 Think ,
- sovereign ,
- reasoning IFM ,
- foundation model ,
- K2 ,
- Institute of Foundation Models ,
- llm ,
Eric Xing explores the ‘next phase of intelligence’ at Davos
Speaking at the World Economic Forum in Davos, MBZUAI President and University Professor Eric Xing looked ahead.....
- WEF ,
- foundation models ,
- Eric Xing ,
- intelligence ,
- panel ,
- Davos ,